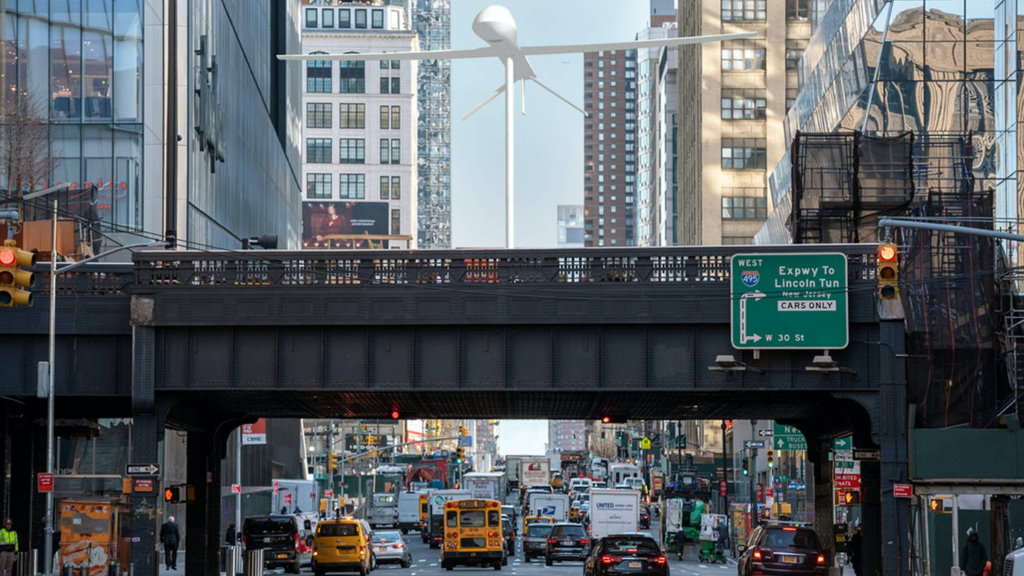

At the High Line, a popular tourist attraction in New York City, visitors to the West side of Lower Manhattan ascend above street level to what was once an elevated freight train line and is now a tranquil and architecturally intriguing promenade. Here walkers enjoy a park-like openness; with fellow strollers they experience urban beauty, art and the wonder of comradeship.
In late May, a Predator drone replica, appearing suddenly above the High Line promenade at 30th Street, might seem to scrutinize people below. The “gaze” of the sleek, white sculpture by Sam Durant, called “Untitled (drone),” in the shape of the U.S. military’s Predator killer drone, will sweep unpredictably over the people below, rotating atop its 25-foot-high steel pole, its direction guided by the wind.
Unlike the real Predator, it won’t carry two Hellfire missiles and a surveillance camera. The drone’s death-delivering features are omitted from Durant’s sculpture. Nevertheless, he hopes it will generate discussion.
“Untitled (drone)” is meant to animate questions “about the use of drones, surveillance, and targeted killings in places far and near,” said Durant in a statement “and whether as a society we agree with and want to continue these practices.”
Durant regards art as a place for exploring possibilities and alternatives.
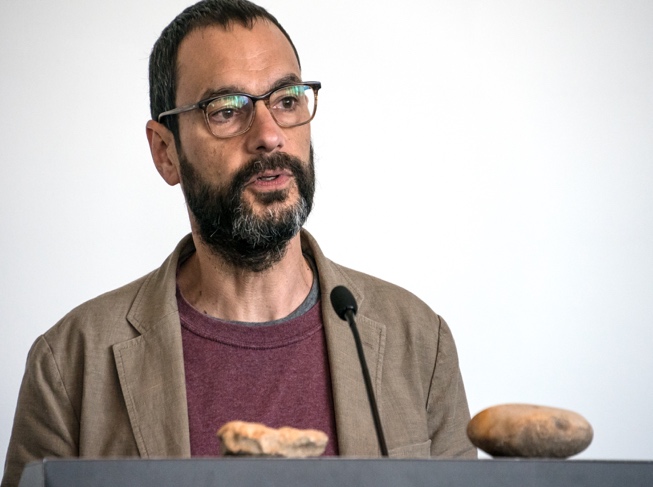

In 2007, a similar desire to raise questions about remote killing motivated New York artist Wafaa Bilal, now a professor at NYU’s Tisch School of the Arts, to lock himself in a cubicle where, for a month, and at any hour of the day, he could be remotely targeted by a paint-ball gun blast. Anyone on the internet who chose to could shoot at him.

He was shot at more than 60,000 times by people from 128 different countries. Bilal called the project “Domestic Tension.” In a resulting book, Shoot an Iraqi: Art, Life and Resistance under the Gun, Bilal and co-author Kari Lydersen chronicled the remarkable outcome of the “Domestic Tension” project.

Along with descriptions of constant paint-ball attacks against Bilal, they wrote of the internet participants who instead wrestled with the controls to keep Bilal from being shot. And they described the death of Bilal’s brother, Hajj, who was killed by a U.S. air-to-ground missile in 2004.
Grappling with the terrible vulnerability to sudden death felt by people all across Iraq, Bilal, who grew up in Iraq, with this exhibit chose to partly experience the pervasive fear of being suddenly, and without warning, attacked remotely. He made himself vulnerable to people who might wish him harm.
Three years later, in June 2010, Bilal developed the “And Counting” art work in which a tattoo artist inked the names of Iraq’s major cities on Bilal’s back. The tattoo artist then used his needle to place “dots of ink, thousands and thousands of them – each representing a casualty of the Iraq war. The dots are tattooed near the city where the person died: red ink for the American soldiers, ultraviolet ink for the Iraqi civilians, invisible unless seen under black light.”
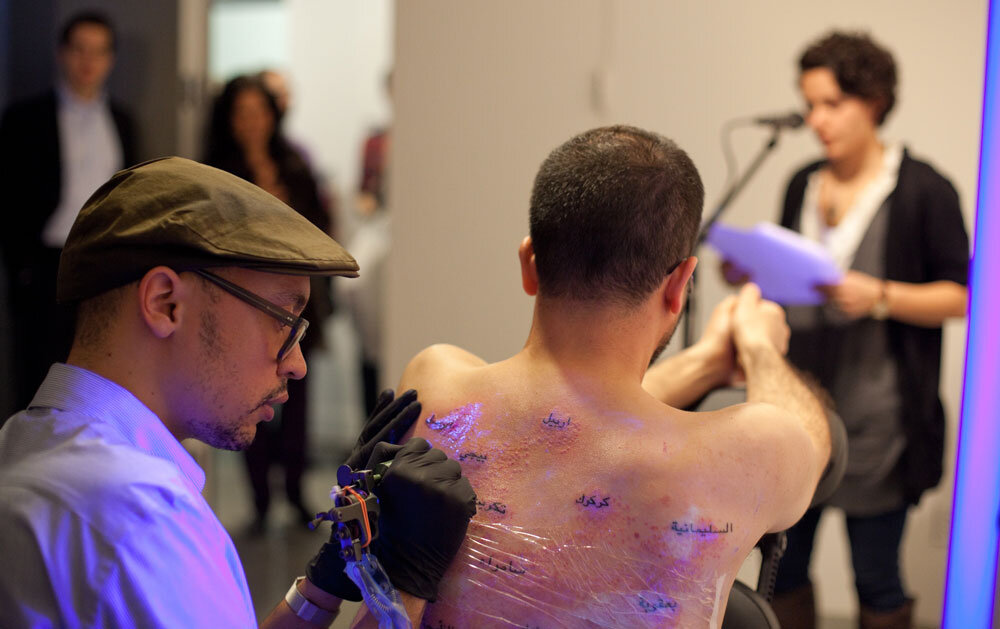
Bilal, Durant and other artists who help us think about U.S. colonial warfare against the people of Iraq and other nations should surely be thanked. It is helpful to compare Bilal’s and Durant’s projects.
The pristine, unsullied drone may be an apt metaphor for twenty-first-century U.S. warfare which can be entirely remote. Before driving home to dinner with their own loved ones, soldiers on another side of the world can kill suspected militants miles from any battlefield. The people assassinated by drone attacks may themselves be driving along a road, possibly headed toward their family homes.
U.S. technicians analyze miles of surveillance footage from drone cameras, but such surveillance does not disclose information about the people a drone operator targets.
In fact, as Andrew Cockburn wrote in the London Review of Books, “the laws of physics impose inherent restrictions of picture quality from distant drones that no amount of money can overcome. Unless pictured from low altitude and in clear weather, individuals appear as dots, cars as blurry blobs.”
On the other hand, Bilal’s exploration is deeply personal, connoting the anguish of victims. Bilal took great pains, including the pain of tattooing, to name the people whose dots appear on his back, people who had been killed.
Contemplating “Untitled (drone),” it is unsettling to recall that no one in the U.S. can name the 30 Afghan laborers killed by a U.S. drone in 2019. A U.S. drone operator fired a missile into an encampment of migrant workers resting after a day of harvesting pine nuts in Afghanistan’s Nangarhar province. An additional 40 people were injured. To U.S. drone pilots, such victims may appear only as dots.
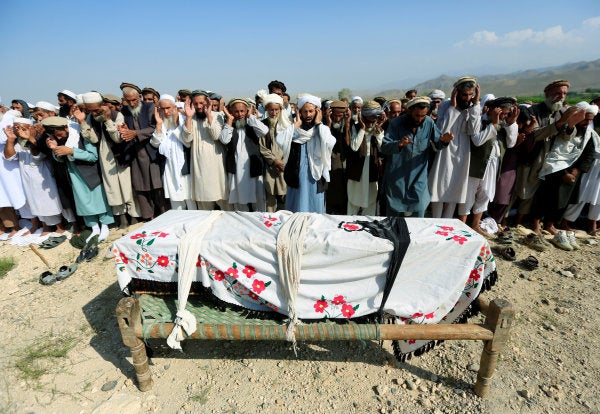

In many war zones, incredibly brave human rights documentarians risk their lives to record the testimonies of people suffering war-related human rights violations, including drone attacks striking civilians. Mwatana for Human Rights, based in Yemen, researches human rights abuses committed by all sides to the war in Yemen. In their report, Death Falling from the Sky: Civilian Harm from the United States’ Use of Lethal Force in Yemen January 2017-January 2019, they examine 12 U.S. aerial attacks in Yemen, 10 of them U.S. drone strikes, between 2017 and 2019.
They report at least 38 Yemeni civilians—19 men, 13 children, and 6 women—were killed and 7 others were injured in the attacks.

From the report, we learn of important roles the slain victims played as family and community members. We read of families bereft of income after the killing of wage earners, including beekeepers, fishers, laborers and drivers. Students described one of the men killed as a beloved teacher. Also among the dead were university students and housewives. Loved ones who mourn the deaths of those killed still fear hearing the hum of a drone.
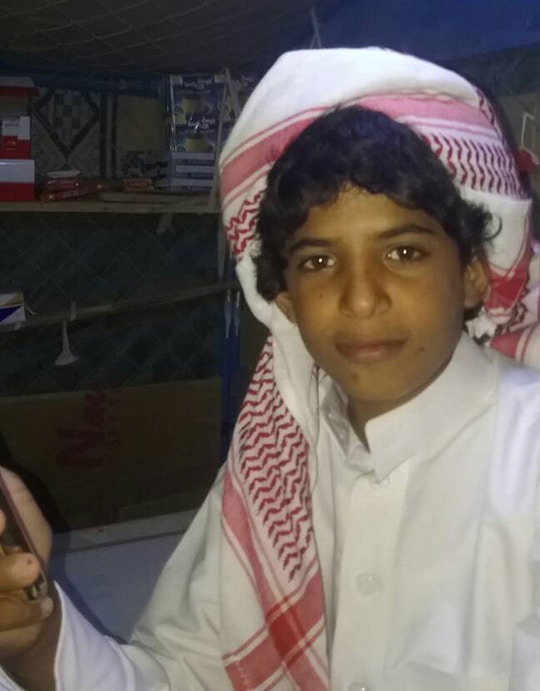

It is now clear that the Houthis in Yemen have been able to use 3-D models to create their own drones which they have fired across a border, hitting targets in Saudi Arabia. This kind of proliferation has been entirely predictable.
The U.S. recently announced plans to sell the United Arab Emirates 50 F-35 fighter jets, 18 Reaper drones, and various missiles, bombs and munitions. The UAE has used its weapons against its own people and has run ghastly clandestine prisons in Yemen where people are tortured and broken as human beings, a fate awaiting any Yemeni critic of its power.

The installation of a drone overlooking people in Manhattan can bring them into the larger discussion.
Outside the gates of many military bases safely within the U.S.—from which drones are piloted to deal death over Iraq, Afghanistan, Yemen, Somalia, Syria and other lands—activists have repeatedly staged artistic events. In 2011, at Hancock Field in Syracuse, 38 activists were arrested for a “die-in” during which they simply lay down, at the gate, covering themselves with bloodied sheets.

The title of Sam Durant’s sculpture – “Untitled (drone)” – means that in a sense it is officially nameless, like so many of the victims of the U.S. Predator drones the sculpture is designed to resemble.
People in many parts of the world cannot speak up. Comparatively, activists living in the U.S. do not face torture or death for protesting. We can tell the stories of the people being killed by our drones, or watching the skies in terror of them. We can “stand with Daniel Hale,” the courageous former Air Force analyst who blew the whistle on the machinery behind and consequences of drone warfare and now faces ten years in prison when he appears before Judge Liam O’Grady on July 27th. We should write to Judge O’Grady and express our gratitude that Hale gave us information crucially necessary for informed decision-making.
We should follow Daniel Hale’s example and share information with our elected representatives while also talking seriously about war to faith-based communities, to academics, to media and to our families and friends.

And if you know anyone in New York City, please tell them to be on the lookout for a Predator drone in Lower Manhattan. This pretend drone could help us grapple with reality and accelerate an international push to ban killer drones.

A version of this article first appeared at The Progressive.org.
CovertAction Magazine is made possible by subscriptions, orders and donations from readers like you.
Blow the Whistle on U.S. Imperialism
Click the whistle and donate
When you donate to CovertAction Magazine, you are supporting investigative journalism. Your contributions go directly to supporting the development, production, editing, and dissemination of the Magazine.
CovertAction Magazine does not receive corporate or government sponsorship. Yet, we hold a steadfast commitment to providing compensation for writers, editorial and technical support. Your support helps facilitate this compensation as well as increase the caliber of this work.
Please make a donation by clicking on the donate logo above and enter the amount and your credit or debit card information.
CovertAction Institute, Inc. (CAI) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization and your gift is tax-deductible for federal income purposes. CAI’s tax-exempt ID number is 87-2461683.
We sincerely thank you for your support.
Disclaimer: The contents of this article are the sole responsibility of the author(s). CovertAction Institute, Inc. (CAI), including its Board of Directors (BD), Editorial Board (EB), Advisory Board (AB), staff, volunteers and its projects (including CovertAction Magazine) are not responsible for any inaccurate or incorrect statement in this article. This article also does not necessarily represent the views the BD, the EB, the AB, staff, volunteers, or any members of its projects.
Differing viewpoints: CAM publishes articles with differing viewpoints in an effort to nurture vibrant debate and thoughtful critical analysis. Feel free to comment on the articles in the comment section and/or send your letters to the Editors, which we will publish in the Letters column.
Copyrighted Material: This web site may contain copyrighted material the use of which has not always been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. As a not-for-profit charitable organization incorporated in the State of New York, we are making such material available in an effort to advance the understanding of humanity’s problems and hopefully to help find solutions for those problems. We believe this constitutes a ‘fair use’ of any such copyrighted material as provided for in section 107 of the US Copyright Law. You can read more about ‘fair use’ and US Copyright Law at the Legal Information Institute of Cornell Law School.
Republishing: CovertAction Magazine (CAM) grants permission to cross-post CAM articles on not-for-profit community internet sites as long as the source is acknowledged together with a hyperlink to the original CovertAction Magazine article. Also, kindly let us know at info@CovertActionMagazine.com. For publication of CAM articles in print or other forms including commercial internet sites, contact: info@CovertActionMagazine.com.
By using this site, you agree to these terms above.
About the Author

Kathy Kelly is a peace activist and author whose efforts to end military and economic wars have sometimes led her to live in war zones and U.S. federal prisons.
She can be reached at kathy.vcnv@gmail.com.





