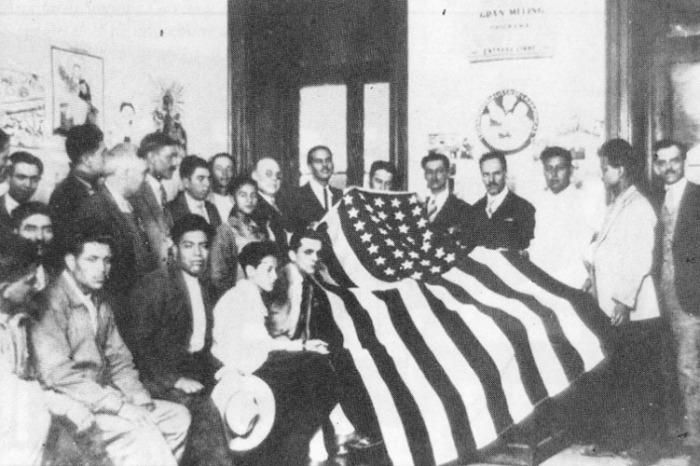

Most Americans Don’t Know About the Real Patriots Who Opposed the Nation’s Forever Wars Going Back to the 19th Century
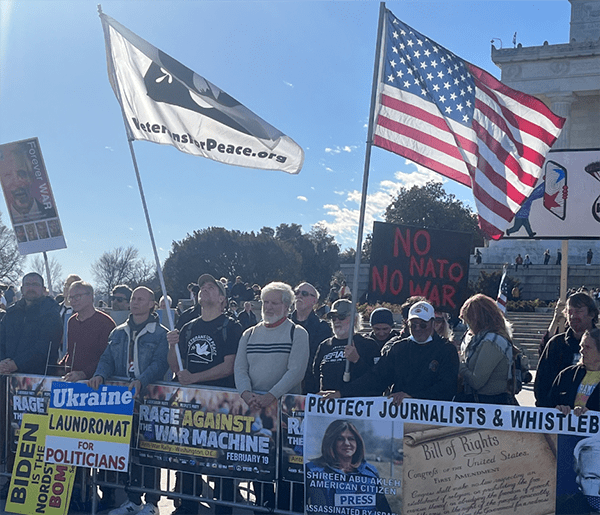
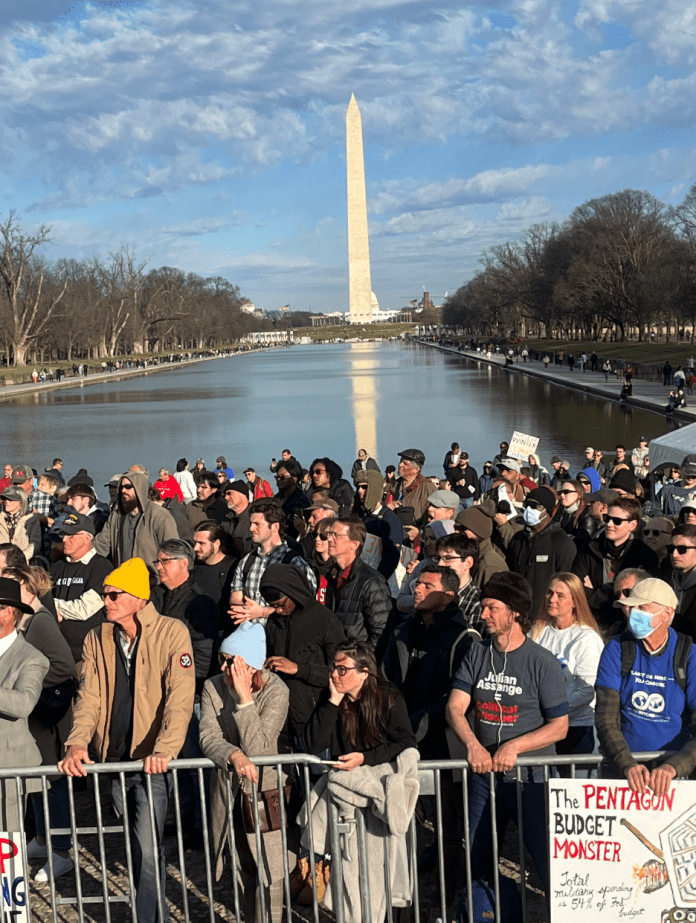
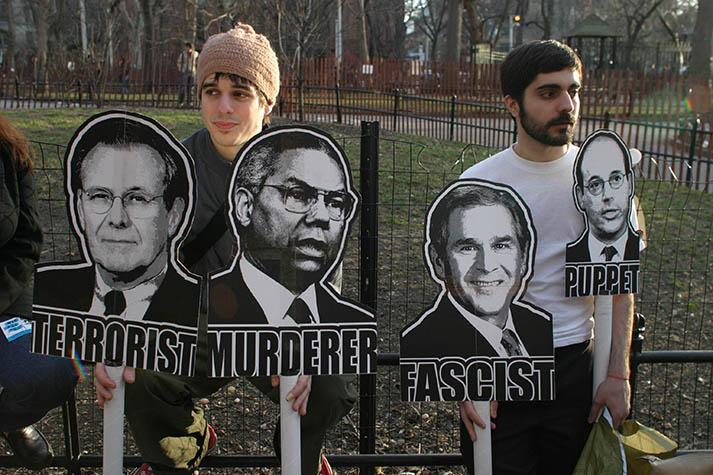
On February 20, journalist Max Blumenthal gave a powerful address at the Rage Against the War Machine rally across from the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C., in which he emphasized how Ukrainians had been used as pawns to advance U.S. imperial interests.
Blumenthal said that people on the other side of the U.S. empire did not care whether people identified as leftist or rightist—what they wanted was for people in the U.S. to “rage against the sick, satanic, neo-conservative war machine” that has caused so much destruction.

Blumenthal was followed on the podium by journalist Chris Hedges, who emphasized that the Ukraine War had been waged by the same intellectually dishonest “high priests of empire” who had advanced the original Cold War and War on Terror. These “pimps of war never see the corpses of their victims”; subscribe to “delusional fantasies”; and are “parasites vomited up in the dying days of empire.”[1]

Blumenthal and Hedges were carrying on the tradition of homegrown anti-imperialism in the U.S. that is too often left out of history textbooks, school curricula and historical commemorations.
The right wing that has tried to block the teaching of critical race theory in schools would surely try to censor the teaching of the history of anti-imperialist movements in the U.S.—if it were actually taught. Most teachers may not know about it or partake in self-censorship out of fear of being branded “anti-American.”
But the anti-imperialist tradition is very much in line with the spirit of the nation’s founding in rebellion against one of the most brutal imperialist powers of its day: Great Britain, which the U.S. has since replaced.
This article will spotlight anti-imperialist resistance to four unjust U.S. wars. The people opposing those wars present excellent role models for today’s growing anti-imperialist movement which was vividly on display at the Rage Against the War Machine rally in Washington, D.C., this past February.

The Mexican-American War
The Mexican-American War foreshadowed the Vietnam War as one of the most unjust wars in history; it lies at the root of the inequality between the U.S. and Mexico.
According to an essay by Roger Peace on a remarkable Peace History website, the war originated as a result of a) a dispute over the border of Texas; and b) the Polk administration’s desire to acquire Mexico’s northern territories of Alta California and Nuevo Mexico.
The Polk administration initiated hostilities when it imposed a naval blockade of the Rio Grande River and had the Texas Rangers engage in provocative maneuvers, though President Polk disingenuously claimed that the U.S. had to fight the war in self-defense. Initially, many U.S. citizens supported the war, with the All of Mexico Movement demanding the annexation of all of Mexico. The slogan, “Remember the Alamo!” was used as a way to fuel anger and to motivate Texans to fight.

Major Danny Sjursen, writing for Truthdig, explained that the slogan “remains a potent battle cry, especially in Texas, but also across the American continent. In the comforting tale, a myth really, [200] Texans, fighting for their freedom against a dictator’s numerically superior force, lost a battle but won the war—inflicting such losses that Mexico’s defeat became inevitable. Never is the word ‘slavery’ or the term ‘illegal immigration’ mentioned. There is no room in the legend for critical thinking or fresh analysis.”

White settlement and the resulting clash between the Mexican army and U.S. citizens culminated in the “Texas War of Independence,” which was a victory for the United States. The president of Mexico, Antonio López de Santa Anna, was forced to sign a treaty which gave the territory of Texas to the U.S. The Mexican Congress dismissed the treaty. But the Mexican Army was in no condition to successfully recapture Texas, although it tried. “Texas was ‘free,’ and a thrilled—and no doubt proud—President [Andrew] Jackson recognized [the] Republic of Texas…” Eventually, 125,000 (mostly Anglo) U.S. citizens poured into Texas with 27,000 slaves.


In 1844, slaveholder James Polk won the U.S. presidential election, defeating Henry Clay of the Whig Party: “Clay preferred restraint with Texas and Mexico. Unfortunately for the Mexicans, Clay was defeated, and the expansionist Polk took office in 1845.”
There were 9,200 men who deserted the U.S. Army in Mexico. Some joined the Mexican Army. “Dozens were later captured and hanged by their former comrades.” War crimes were committed by volunteers in the U.S. Army. “[Gen. Zachary Taylor’s] army of mostly volunteers regularly pillaged villages, murdering Mexican citizens either for retaliation or sport. Many regular Army officers decried the behavior of these volunteers, and one officer wrote, ‘The majority of volunteers sent here are a disgrace to the nation.’”

Representative Luther Severance ridiculed Polk’s claim that American blood was spilt on American soil, the latter being a falsehood based on the conquering of Mexican territory. Severance exclaimed, “[i]t is on Mexican soil that blood had been shed” and that Mexicans “should be honored and applauded” for their “manly resistance.”

As a congressman from Illinois, Abraham Lincoln opposed Polk’s war: “The President, in his first war message of May 1846, declares that the soil was ours on which hostilities were commenced by Mexico; now I propose to try to show, that the whole of this is, from beginning to end, the sheerest deception.” Lincoln expressed his opposition in Congress by presenting Polk’s claims and refuting them.
Lincoln concluded with the following:
“But now, at the end of about twenty months, during which time our arms have given us the most splendid successes–every department, and every part, land and water, officers and privates, regulars and volunteers doing all that men could do, and the hundreds of things which it ever before been thought men could not do–after all this, this same president gives us a long message, without showing us, as to the end, he himself, has, even an imaginary conception. He is a bewildered, confounded, and miserably perplexed man.”

Henry David Thoreau, famous for living at Walden Pond in a hut and as a result lived off the land and wrote there, was a fierce opponent of the war, as well as opposing slavery. Thoreau wrote a manifesto titled “Civil Disobedience,” where he asserts that, to act against the war and slavery was just and necessary:
“In other words, when a sixth of the population of a nation, which has undertaken to be the refuge of liberty, are slaves, and a whole country [Mexico] is unjustly overrun and conquered by a foreign army, and subjected to military law, I think that it is not too soon for honest men to rebel and revolutionize.”

Ulysses S. Grant was a lieutenant at the time and expressed opposition to the war and annexation:
“Generally, the officers of the army were indifferent whether annexation was consummated or not; but not so all of them. For myself, I was bitterly opposed to the measure, and to this day regard the war as one of the most unjust ever waged by a stronger against a weaker nation. Texas was originally a state belonging to the republic of Mexico.”
This opposition from soldiers like Grant was a monumental occasion, since it was the first time there was dissent by U.S. citizens against a U.S.-provoked war. It paved the way for other anti-war movements in the future, some of which were led by ex-soldiers.

The Philippine-American War
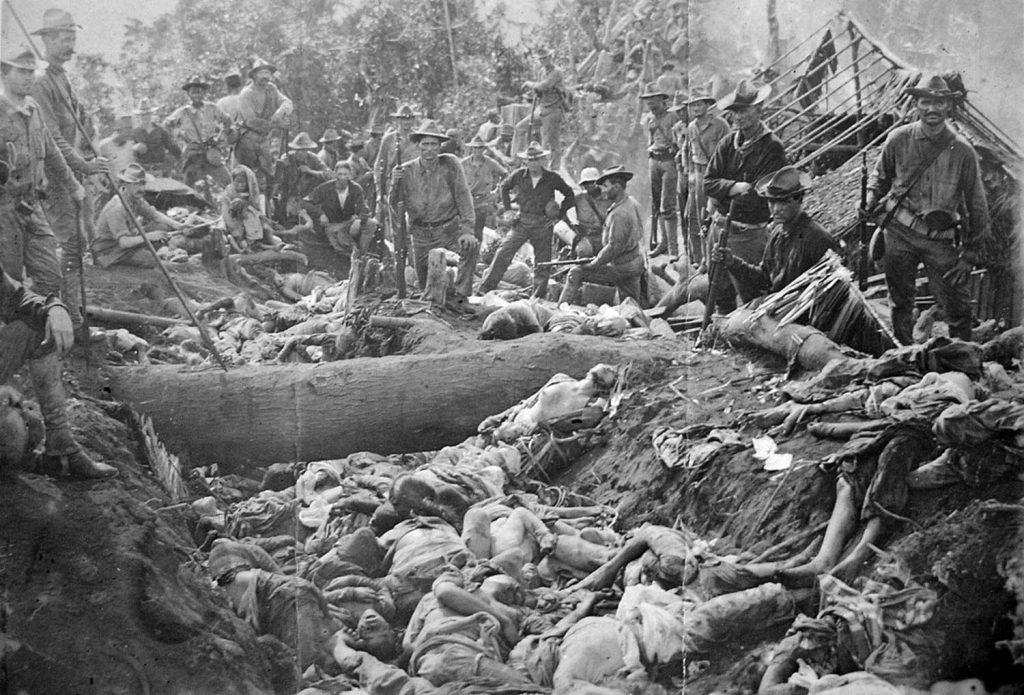
After the defeat of Spain in the Spanish-American War, the Philippines was free of Spanish colonialism, and wanted to establish its First Republic. But the United States, after reassuring the Filipinos that it supported Philippine independence, did the opposite. Similar to the Mexican-American War, U.S. forces committed a number of atrocities such as torture, murder, forced relocation, etc. in what culminated into the Philippine-American War.
In Santa Clara University’s Historical Perspectives, a journal of history, Andrew Clem, originally from the Philippines, wrote a paper that accurately called it “The Filipino Genocide.” Clem revealed what U.S soldiers said about Filipinos, calling them “n_______,” and “monkeys.” Clem went further: “Being depicted as animals, children, or even devils, was unfortunately reflected in American action against Filipinos.”

The Filipinos, with their goal of independence quashed by U.S. deception, took up arms and formed a revolutionary army. Emilio Aguinaldo, president of the First Republic, led the army to stop the U.S. invasion. The Filipinos used conventional warfare initially, but were at a disadvantage because of the formidable weapons of U.S. forces.
The revolutionary army then tried guerrilla warfare in an attempt to wear down the enemy. As Clem wrote: “This strategy, while probably the only means of fighting the superior American forces, also resulted in atrocities. The American military was not constrained by the typical rules of warfare. If the Filipinos were unable to be a part of an American-based society, they would be exterminated.” (The Final Solution?)
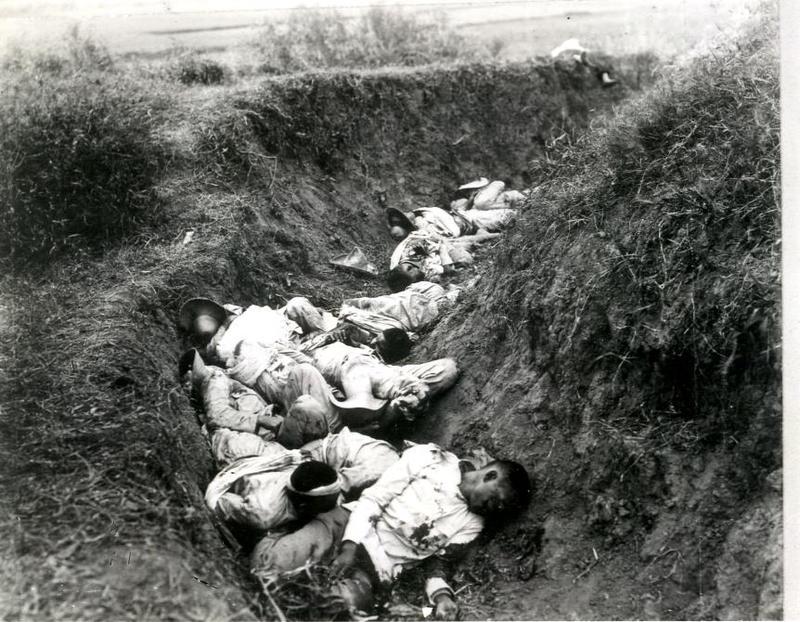

Clem further wrote, “American empire building coupled with widespread racism and the excuse of total war permitted the use of extreme measures such as relocation, concentration camps, and torture. This set the conditions for and inevitably resulted in the genocide of the people residing in the Philippines.”
In the Berkeley News, Ivan Natividad interviewed cultural studies professor Dylan Rodriguez, a first-generation U.S. citizen, about the consequences of war in the Philippines. Natividad quoted Rodriguez: “They [U.S. forces] exterminated entire villages, including elderly people, children and everybody in between. These were war crimes, and the U.S. military was unapologetic and proud of its actions. The narratives that valorize the U.S. are fraudulent….it has been over 100 years, and the United States has still not acknowledged this genocidal conquest.”
During the war, a small but vocal opposition called out the U.S. The Anti-Imperialist League was created in the U.S. in 1898. Its platform strongly opposed U.S. imperialism:
“We hold that the policy known as imperialism is hostile to liberty and tends toward militarism. We maintain that governments derive their just powers from the consent of the governed.
“We earnestly condemn the policy of the present national administration in the Philippines. We deplore the sacrifice of our soldiers and sailors, whose bravery deserves admiration even in an unjust war. We denounce the slaughter of the Filipinos as a needless horror.
“We urge that Congress be promptly convened to announce to the Filipinos our purpose to concede to them the independence for which they have so long fought and which of right is theirs…Imperialists assume that with the destruction of self-government in the Philippines by American hands, all opposition here will cease. This is a grievous error. Much as we abhor the war of “criminal aggression” in the Philippines, greatly as we regret that the blood of the Filipinos is on American hands, we more deeply resent the betrayal of American institutions at home.”


U.S. powerbrokers were considering annexing the Philippines, something which the League condemned.
One of the more well-known members of the Anti-Imperialist League was author and lecturer Mark Twain. The following were his views about the Philippines:
New York Herald, October 15, 1900 –
“I left these shores, at Vancouver, a red-hot imperialist. I wanted the American eagle to go screaming into the Pacific. Why not spread its wings over the Philippines, I asked myself? And I thought it would be a real good thing to do.

“But I have thought some more, since then, and I have seen that we do not intend to free, but to subjugate the people of the Philippines. We have gone there to conquer, not to redeem.
“And, so, I am an anti-imperialist. I am opposed to having the eagle put its talons on any other land.”
A 1906 essay, published after his death:
“General Wood was present and looking on. His order had been, ‘Kill or capture those savages.’ Apparently our little army considered that the ‘or’ left them authorized to kill or capture according to taste, and that their taste had remained what it has been for eight years in our army out there—the taste of Christian butchers.”

A February 1901 article titled, “To the Person Sitting in Darkness” –
“There must be two Americas: one that sets the captive free, and one that takes a once-captive’s new freedom away from him, and picks a quarrel with him with nothing to found it on; then kills him to get his land. We have robbed a trusting friend of his liberty; we have debauched America’s honor and blackened her face before the world.
“And as for a flag for the Philippine Province, it is easily managed. We can have a special one: we can have our usual flag, with the white stripes painted black and the stars replaced by the skull and cross-bones.”
One individual who has been virtually an unknown to the U.S. establishment (but known in the Black community in the 1900s) was David Fagen, an African-American soldier sent to the Philippines along with others who were known as “Buffalo Soldiers.”
Fagen was originally from Tampa, Florida, and experienced overt racism there. Writing for CounterPunch, Jonathan Melrod asserted that Fagen “grew up where Jim Crow segregation laws prevailed. With the specter of lynching, race riots and the chain gang looming over Tampa’s Blacks, Fagen ‘lived in dread at all times.’”
Deciding to escape the racism, Fagen enlisted in the military, the 24th Infantry Regiment, “a unit of so-called Buffalo Soldiers,” who numbered 2,100 out of 6,000 African-American soldiers who were sent to the Philippines. Fagen and other Blacks continued to experience racism in the ranks of the army. There were clashes between Fagen and white commanding officer Lt. James A. Moss, a West Point graduate. From that, Fagen hated the commanding officer. The latter in turn punished Fagen for stepping out of line.
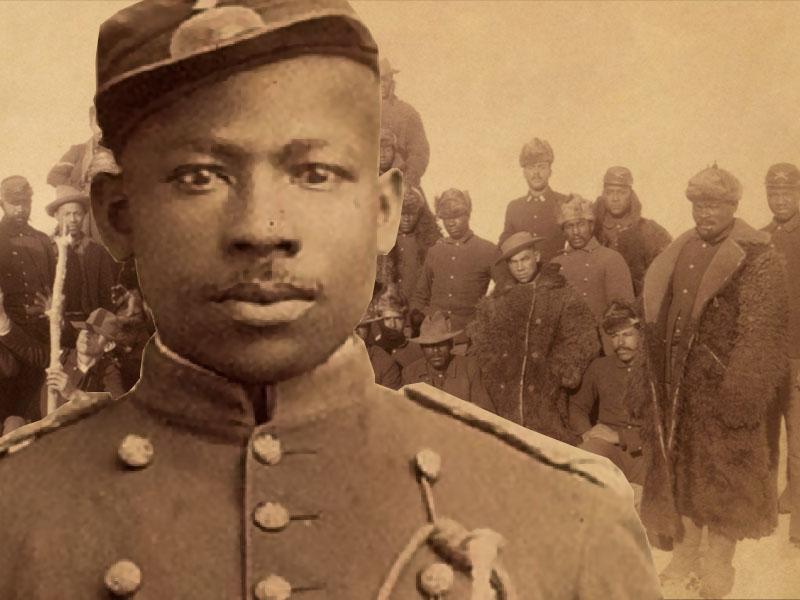

African-American soldiers were expendable, treating them like second-class citizens. It was that and the persuasion of Filipino revolutionaries for Blacks to join their cause, in which Fagen decided to rebel and switch sides.
After all, both African-Americans and Filipinos had the same racist oppressors. Melrod wrote that 15 Buffalo Soldiers defected to the other side. “The ‘deserters’ of the 24th infantry proved one thing: systemic racism and oppression by white Americans was enough to forge alliances across vast national and ethnic lines.”
According to Melrod, “Fagen was never captured or killed.” While the U.S. military considered Fagen to be a “deserter and traitor,” Filipinos respected him as a guerrilla leader.
It is said that Fagen eventually fell in love with a Filipina and both went into the mountains and lived a peaceful life.
The Vietnam War

The Vietnam War was a moral abomination, which resulted in the deaths of between two and five million Vietnamese civilians along with 58,000 U.S. soldiers and the destruction of much of the Vietnamese countryside.
The U.S. first became involved in Vietnam when the Truman and Eisenhower administrations supported France’s war of colonial re-conquest. The Eisenhower administration then subverted the Geneva Accords that called for elections that would unify Vietnam because it knew that Vietnamese Communist leader Ho Chi Minh would win those elections.
The Eisenhower administration in turn began trying to build a client regime in South Vietnam under Catholic anti-communist Ngo Dinh Diem who was assassinated in 1963 after he made overtures toward peace with North Vietnam.

The Kennedy administration expanded the war, sending 16,000 military advisers while intensifying bombing operations in South Vietnam and initiated aerial defoliation operations in an attempt to destroy the forest cover of the National Liberation Front (NLF-southern based guerrillas nicknamed “Vietcong”).
The Johnson administration ordered a full-scale U.S. military invasion after falsely claiming that a U.S. naval ship had suffered an unprovoked attack on the South China Sea (the Gulf of Tonkin incident). [As a young history teacher, President Lyndon B. Johnson had taught students a romanticized view of the Texas revolution and viewed the Vietnamese similarly to the Mexicans; socially inferior beings who should easily be bended to the American will).
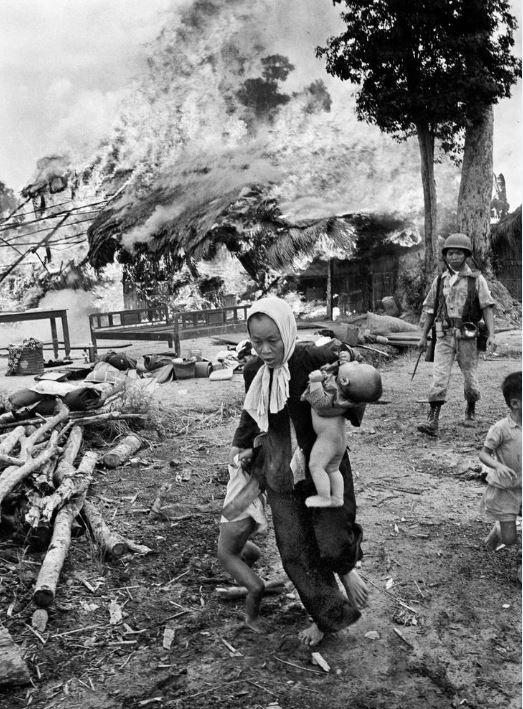

Anti-war opposition was very limited in the 1950s and early 1960s, confined to dedicated activists like Reverend A.J. Muste who suffered from societal ostracism in the heart of the McCarthy era.

However, as news reports of the horrors in Vietnam spread, people in the 1960s began speaking out. Soon, there was talk of rebellion and revolution. And the rank-and-file of the U.S. military were not immune to it.
There were, for example, conscientious objectors who resisted the military draft, which mainly obligated minorities and low and middle-class whites to join the military and fight for a false cause.
Demonstrations in 1965 started a groundswell of protest, the main reason being the escalation of more troops going to Vietnam, thanks to Lyndon Johnson.
The protests tied into other movements, like African-American civil rights, feminism and organized labor. The anti-war movement, combined with the other movements, sparked controversy and fervent debate in the U.S., virtually shaking the foundations of the establishment. Protesters chanted “Hell, no, we won’t go!” and “1,2,3,4, we don’t want your fucking war!”

GIs increasingly became disillusioned with the war, seeing it more as a means for their country to conquer territory, rather than promoting freedom and democracy. The pro-war excuse was that communism would spread all over Southeast Asia, this being called the domino theory (countries would fall like dominos). GIs rejected this, and instead rebelled against the U.S.’s imperial objectives.

A major revelation occurred when Daniel Ellsberg leaked the Pentagon Papers, a collection of secret government planning documents, which showed how the American public had been lied to and that the war was un-winnable.
The Nixon administration was determined to stop the leaks. Nixon’s Attorney General, John Mitchell, demanded that The New York Times halt publication. The Times refused, and the government sought a restraining order to prevent it from publishing the documents. The Times won the case. In the meantime, Ellsberg leaked the documents to other newspapers.
Ellsberg was adamant in saying what the truth was about the Vietnam War:
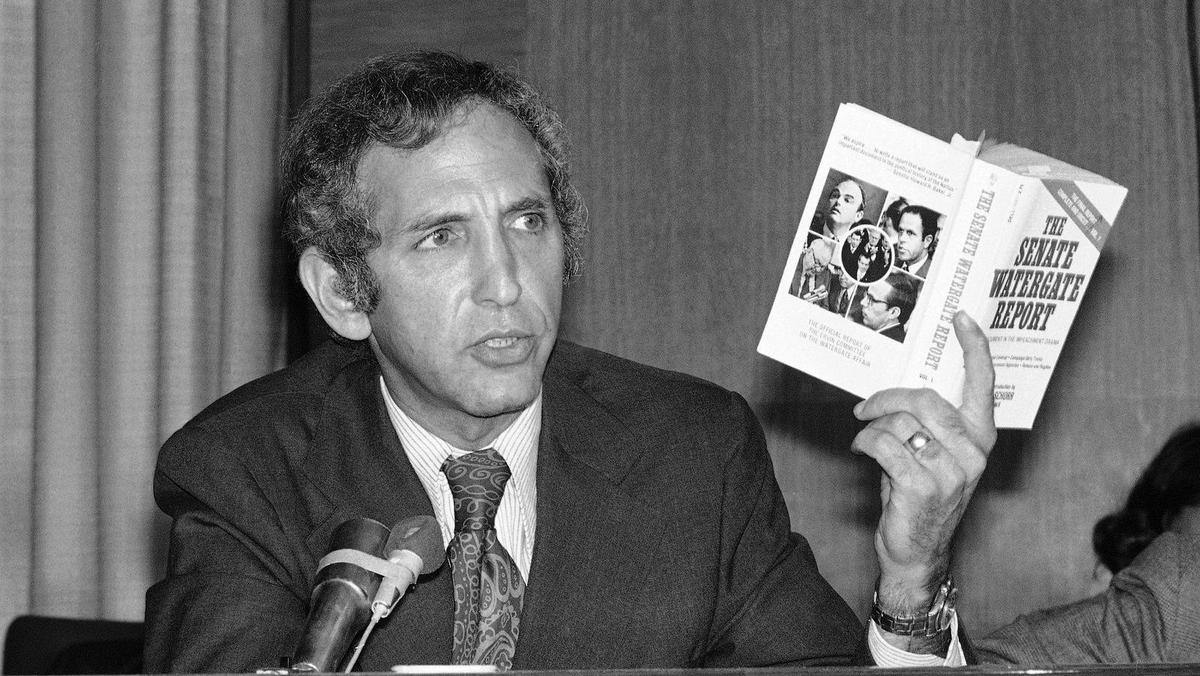

“It was no more a ‘civil war’ after 1955 or 1960 than it had been during the U.S.-supported French attempt at colonial reconquest. A war in which one side was entirely equipped and paid by a foreign power – which dictated the nature of the local regime – was not a civil war. To say that we had ‘interfered’ in what is ‘really a civil war,’ simply screened a more painful reality and was as much a myth as the earlier official one of ‘aggression from the North.’ In terms of the UN Charter and of our own ideals, it was a war of foreign aggression, American aggression.”
A major factor was the formidable opposition to it. Rebellion and resistance reached a level where it could not be denied, or stopped.
The Iraq War
Because of the U.S.’s imperial foreign policy, lies from the government and the media have remained consistent. It was blatant where the George W. Bush regime is concerned. Lying became an Orwellian act. The often-used right-wing slogan “Freedom isn’t Free!” bears this out. It was as pathetic as the renaming of French fries into “Freedom Fries.”
Unfortunately, many citizens in the U.S. were at first gung-ho about the Iraq war. According to the Pew Research Center, 73% of U.S. citizens supported the war in 2002, before it was launched. At the same time, hundreds of thousands of Americans took to the streets in cities across the country to protest the war in an unprecedented antiwar display.

Bush and others in his administration claimed that Saddam Hussein harbored WMDs, had ties to al-Qaeda, and was involved in the 9/11 attacks. The regime was sure these accusations would sway the U.S. public to support war.
Two examples of such accusations were:
Vice President Dick Cheney’s speech to the VFW, saying, “Simply stated, there is no doubt Saddam Hussein now has weapons of mass destruction. There is no doubt he is amassing them to use against our friends, our allies, and us.”
Colin Powell, Secretary of State, made a shameful presentation to the UN, claiming, there were “facts and conclusions based on solid evidence” that Iraq did not comply with UN weapons inspections. Powell added, “Leaving Hussein in possession of [WMDs] for a few more months or years is not an option, not in a post-September 11 world.”

The U.S. empire’s war began in 2003, with the Bush Jr. regime boasting that it would result in “shock and awe.” Most U.S. leaders like to condemn others for terrorist acts, but what the empire did in Iraq was a form of terrorism. Predictably, an Iraqi resistance formed to combat U.S. soldiers and ensured that the war dragged on in a quagmire like Vietnam.
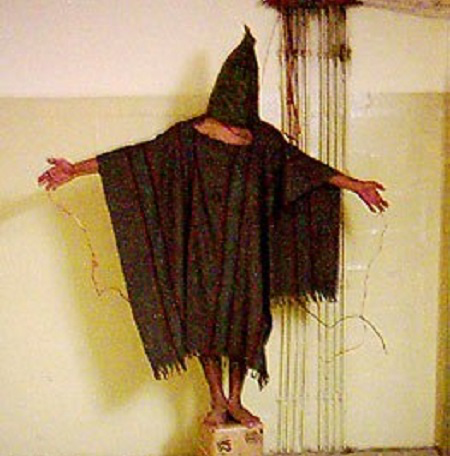
Public opinion shifted irrevocably against the war following revelations about torture committed by U.S. troops in the barbaric Abu Ghraib prison. Photos of torture were posted on the internet by individuals who could only be described as sadists.

By 2007, about 54% of Americans were against sending more troops to Iraq. Both GIs and civilians had become outraged by the obvious illegality of the war and revelations of U.S. atrocities and war crimes.

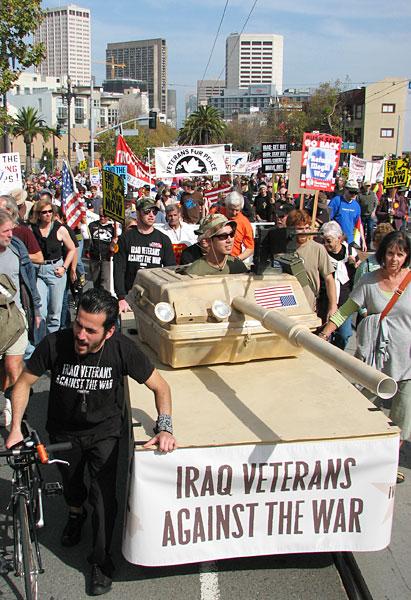
Veterans Against the War made it known that the war was based on lies. In their publication called About Face, it stated that “terror will rain from the sky upon the people of Iraq, violence will flood the streets of a sovereign nation, and 7,000 miles away U.S. politicians and media will lockstep in their lies to justify it all.”
It continued: “we were lied into the war by politicians shilling for war-profiteering contractors, [and] incalculable Iraqi lives were cut short or forever changed. Though George W. Bush and his cronies may wish to repaint their images from blood-thirsty barons to affable retirees, we must continue to accurately recount the Bush administration’s role in manufacturing societal consent for war.”
The publication goes on to condemn the “War on Terror,” the “so-called ‘Defense Budget,’” and condemning “war profiteering contractors like Boeing, Raytheon, and Lockheed Martin.”
Just as important, the publication mentioned the worldwide protests against the war: “We must continue to tell the stories of the nearly 36 million people worldwide who protested the U.S.-led invasion of Iraq, the stories of countless dissenting veterans who put down their [arms] in Iraq,” and to “continue to tell the stories of the millions of Iraqis killed or traumatized by U.S.-led terror who are still fighting for self-determination.”
In a piece published in Al Jazeera, veterans offered their feedback on the war. Naveed Shah, like many recruits, was inspired to enlist after the 9/11 attacks. He joined the army in 2006, oblivious to the Bush Jr. regime’s lies about Iraq. But on the 20th anniversary of the Iraq War, Shah was not so gung-ho: “The war was based on a lie. It was wrong for us to be there in the first place.”
Kristofer Goldsmith served in Iraq and now has regrets: “My year in Iraq wasn’t pleasant. I can’t say any American, much less any Iraqi, is better off for me having served there.” Eventually, Goldsmith was discharged after attempting suicide: “When I left the military, I lost a big part of my identity. Sharing my story and my experiences really helped me get out of a dark place.”
Al Jazeera cited a poll by the Pew Research Center conducted in 2019. It found that 64% of veterans thought the war was not worth fighting. For all U.S. adults, 62% agreed.

It is evident that the military-industrial complex has not learned any lessons about war. Ukraine is an example of the U.S. funding a proxy war that is in essence an imperial war which has its supporters sadly on the left.
Those who do not support the war are ostracized by these groups. It is a case of “either you are with us or against us.”
The U.S., as an empire, must be opposed because it causes vast amounts of devastation all around the world and is sustained by violent political coercion and deception.
This fact has been recognized by anti-imperialists who should be regarded as visionaries that care about people around the world and would like to see their country behave in a more civilized and decent way.

- Read Jeremy Kuzmarov’s article titled “Left and Right Join Together to Express Anger Against Ukraine War on Its One Year Anniversary” published in CovertAction Magazine on February 20, 2023. You can find the article at the following link: https://covertactionmagazine.com/2023/02/20/left-and-right-join-together-to-rage-against-ukraine-war-on-its-one-year-anniversary/
CovertAction Magazine is made possible by subscriptions, orders and donations from readers like you.
Blow the Whistle on U.S. Imperialism
Click the whistle and donate
When you donate to CovertAction Magazine, you are supporting investigative journalism. Your contributions go directly to supporting the development, production, editing, and dissemination of the Magazine.
CovertAction Magazine does not receive corporate or government sponsorship. Yet, we hold a steadfast commitment to providing compensation for writers, editorial and technical support. Your support helps facilitate this compensation as well as increase the caliber of this work.
Please make a donation by clicking on the donate logo above and enter the amount and your credit or debit card information.
CovertAction Institute, Inc. (CAI) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization and your gift is tax-deductible for federal income purposes. CAI’s tax-exempt ID number is 87-2461683.
We sincerely thank you for your support.
Disclaimer: The contents of this article are the sole responsibility of the author(s). CovertAction Institute, Inc. (CAI), including its Board of Directors (BD), Editorial Board (EB), Advisory Board (AB), staff, volunteers and its projects (including CovertAction Magazine) are not responsible for any inaccurate or incorrect statement in this article. This article also does not necessarily represent the views the BD, the EB, the AB, staff, volunteers, or any members of its projects.
Differing viewpoints: CAM publishes articles with differing viewpoints in an effort to nurture vibrant debate and thoughtful critical analysis. Feel free to comment on the articles in the comment section and/or send your letters to the Editors, which we will publish in the Letters column.
Copyrighted Material: This web site may contain copyrighted material the use of which has not always been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. As a not-for-profit charitable organization incorporated in the State of New York, we are making such material available in an effort to advance the understanding of humanity’s problems and hopefully to help find solutions for those problems. We believe this constitutes a ‘fair use’ of any such copyrighted material as provided for in section 107 of the US Copyright Law. You can read more about ‘fair use’ and US Copyright Law at the Legal Information Institute of Cornell Law School.
Republishing: CovertAction Magazine (CAM) grants permission to cross-post CAM articles on not-for-profit community internet sites as long as the source is acknowledged together with a hyperlink to the original CovertAction Magazine article. Also, kindly let us know at info@CovertActionMagazine.com. For publication of CAM articles in print or other forms including commercial internet sites, contact: info@CovertActionMagazine.com.
By using this site, you agree to these terms above.
About the Author

David Starr acknowledged his interest in politics in 1986 when he lived in Hawai’i.
From there, he became active, joining such groups as the Latin American and Caribbean Solidarity Association (LACASA), the Hawai’i Union of Socialists (HUS) and Ka Lehui Hawai’i (The Hawaiian Nation).
Starr also created a publication entitled Voices of Change, and had articles published in the Honolulu Weekly and Toward Freedom during the 1990s.
Now Connecticut-based, Starr has published many pieces in Reader Supported News, the Daily Kos, and has been published in the LA Progressive.
David can be reached at dl_starr@hotmail.com.




–
The Republican Party that was formed in 1854 was totally different from the Republican Party of today. It was anti-slavery, anti-establishment, socially progressive party. In fact Abraham Lincoln was influenced by Karl Marx and frequently read books about Karl Marx. But some time during the 20th century the party shifted towards the right and evolved into the present day entity with the likes of Marjorie Taylor Greene and company. The original Republican Party was more similar to today’s Democratic Party.
You are correct about the Republican Party and its initial progression, then its digression. Actually, the GOP started to change in the 1870s when it became a pro-business party. In the 1890s, it was an overtly racist and greedy entity, using Manifest Destiny doctrine to try and conquer other lands. And the rest is history. Now, we continue to have a much worse GOP, but with its use of code words and dog whistles to cover for their racism and fake concern for the working class. And, yes, Abraham Lincoln was probably influenced by Karl Marx. Lincoln once said that labor is the superior of capital and deserves the higher consideration. No doubt he was influenced by Marxist ideas.
According to this website it seemed to occur sometimes during the 1920’s although there are mixed views about this, so it could be much earlier as you say.:
https://www.vox.com/2016/7/20/12148750/republican-party-trump-lincoln
This is what the article says:
We know the Republican Party today as a party that hates government interference with business. But as the 20th century started, progressive reformers who wanted to check the power of corporations and the wealthy had some support in both parties — and notably, from Republican President Theodore Roosevelt.
That didn’t last. When Democrat Woodrow Wilson won the presidency, the Republican Party turned sharply against many of his progressive reforms, which they came to believe expanded government’s power too much. When Republicans regained power and held it throughout the ’20s, they were unmistakably the party of business. They thought prosperity for business was good for America and governed accordingly.
Thank you for the information. Maybe they started becoming pro-business in the 1870s but made it more obvious in the 1920s.